
Maximizing Water Reuse Potential in Industries
As water scarcity continues to be a global concern, industries are increasingly recognizing the importance of sustainable water management. Water reuse, the process of treating and repurposing wastewater, has emerged as a valuable solution to alleviate pressure on freshwater sources. In this blog, we will explore the significance of water reuse in industries, focusing on innovative water treatment on a Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) methodology using technologies such as – Effluent Treatment Plants (ETP), Membrane Bioreactors (MBR), Reverse Osmosis (RO), Ultrafiltration (UF), and Nanofiltration (NF).
The Benefits of Water Reuse
Water reuse offers a range of benefits for industries. By reusing treated wastewater, industries significantly reduce their reliance on freshwater supplies, easing the strain on limited resources and contributing to water conservation efforts. This not only helps mitigate the impact of water scarcity but also promotes responsible water management practices.
Moreover, water reuse enhances operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Integrating water reuse systems, such as ZLD and ETP, enables industries to save on water procurement and treatment costs, while promoting sustainable practices. By utilizing advanced treatment processes, the quality of treated wastewater is improved to meet stringent standards, making it suitable for various non-potable applications.
Innovative Water Treatment Processes and Technologies
- Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD): ZLD is an advanced water treatment approach that eliminates liquid discharge by recovering valuable resources from wastewater. Through processes like evaporation, crystallization, and solid-liquid separation, ZLD systems minimize water waste and maximize resource recovery, making it an ideal solution for industries aiming to achieve sustainability goals.
- Effluent Treatment Plants (ETP): ETPs are designed to treat industrial effluents and remove pollutants before their discharge. These plants employ various treatment processes such as physical, chemical, and biological methods to purify wastewater. By utilizing ETPs, industries can ensure compliance with environmental regulations while minimizing their environmental footprint.
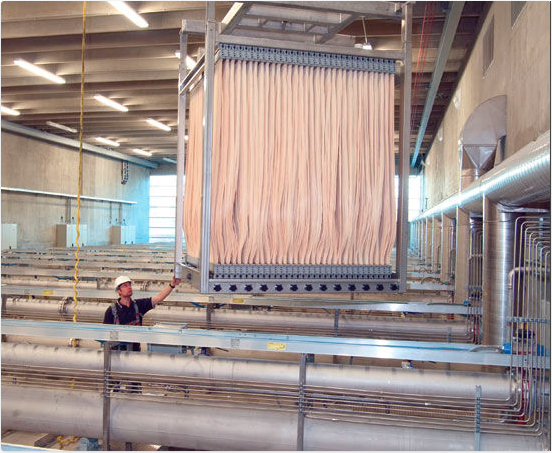
- Membrane Bioreactors (MBR): MBR combines activated sludge treatment with membrane filtration to achieve high-quality wastewater treatment. The process involves microorganisms breaking down organic matter, while membranes with small pores filter out solids, bacteria, and viruses. MBR systems produce treated water that meets strict standards for reuse, making it suitable for industries requiring high-quality process water.
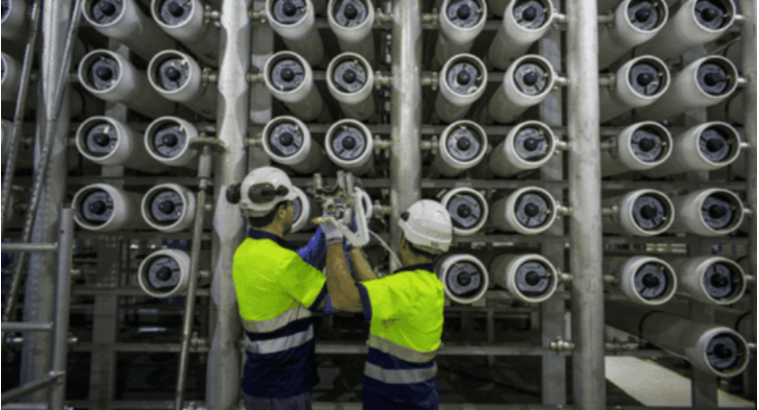
- Ultrafiltration (UF) and Nanofiltration (NF): UF and NF are membrane filtration processes that remove suspended solids, bacteria, and larger molecules from water. UF membranes have larger pores, while NF membranes have smaller pores than UF. Both technologies can be employed in water treatment processes to achieve different levels of filtration, depending on the desired water quality and specific industry requirements.
Water reuse presents a significant opportunity for industries to enhance their water management practices and contribute to sustainable development.
By implementing innovative water treatment processes and technologies such as ZLD, ETP, MBR, UF, and NF, industries can effectively treat wastewater and repurpose it for various non-potable applications. Embracing water reuse not only conserves water resources but also promotes responsible and eco-friendly industrial practices.






About The Author: Pure Water
More posts by Pure Water